Linguistic Features between University Students in California and New York: Reddit Version
Clyde Villacrusis, Sydnie Yu, Monique Tunnell, Michelle Kim
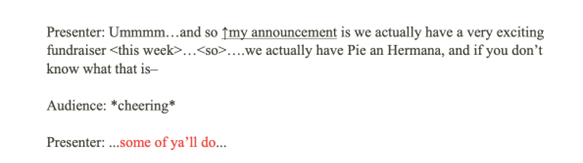
How often do you find yourself saying “hella” or “bet?” How does this differ for people across different regions? The research project discussed in this blog article compares linguistic markers, particularly slang, in Reddit communities of universities in New York and California. Using basic forms of natural language processing, we analyzed posts from multiple university-specific Reddit pages to identify regional slang differences. Results show distinct slang patterns reflecting local cultures — New York slang influenced by its diverse linguistic environment, and California slang shaped by surf and tech cultures. In addition, New York university students have shown that they are less susceptible to slang and jargon, as most of them are out-of-state students and therefore, grew up in a community where it is harder for them to immerse in NY culture and its language. For California students, it is easier for them to immerse in the language culture because most are in-state students. These findings highlight the role of language in forming regional identities in digital spaces, offering insights for sociolinguistic research and digital communication strategies.
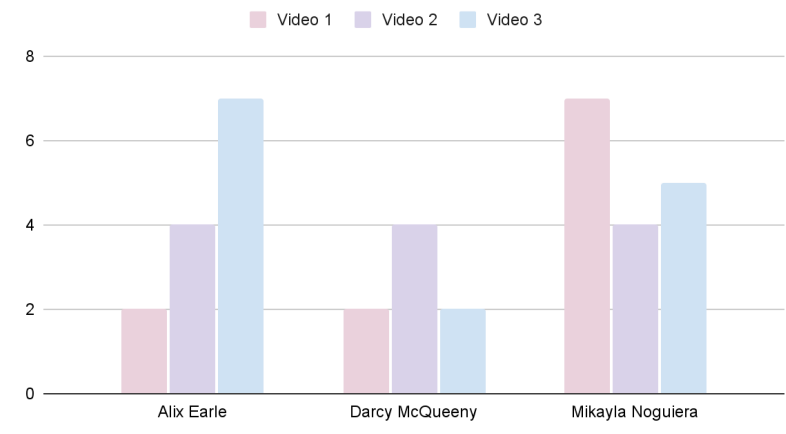
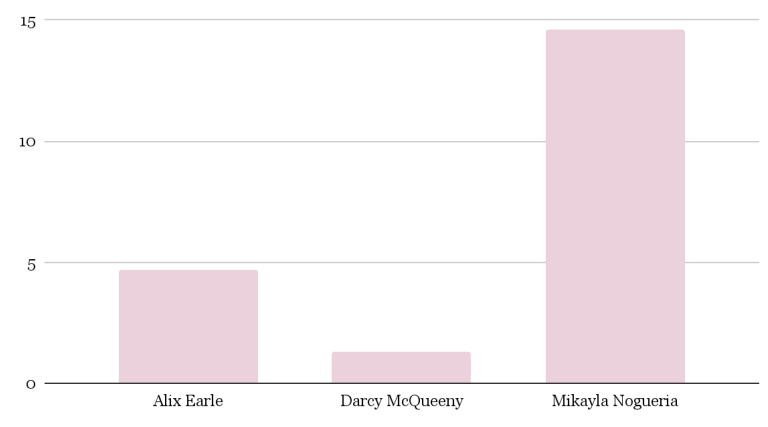
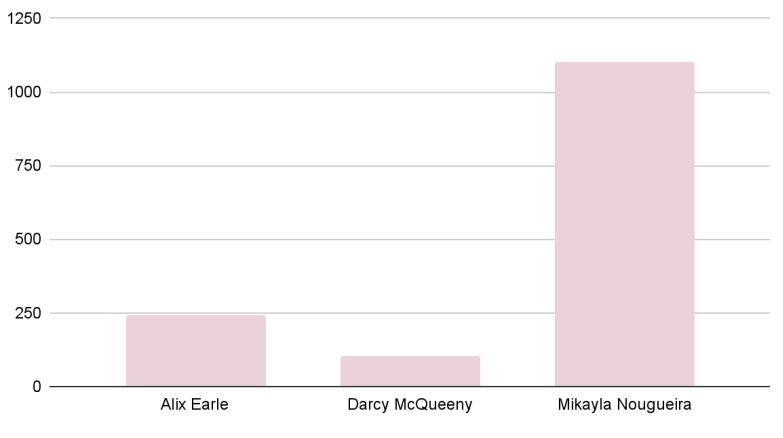
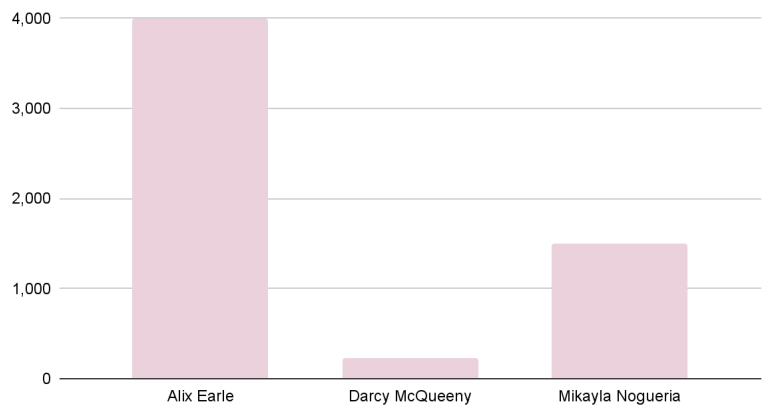
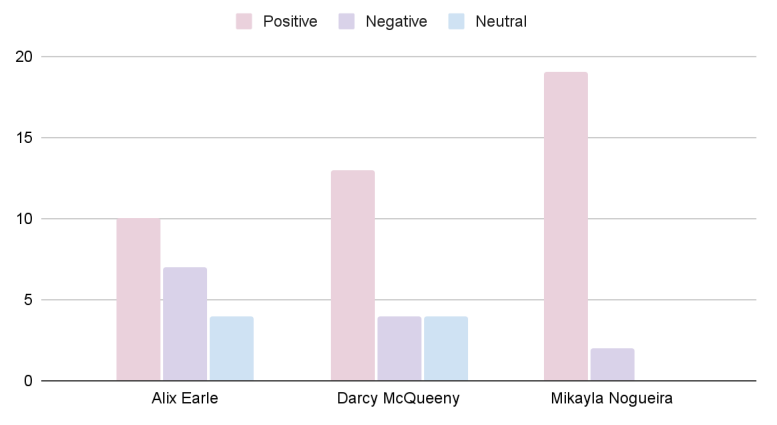
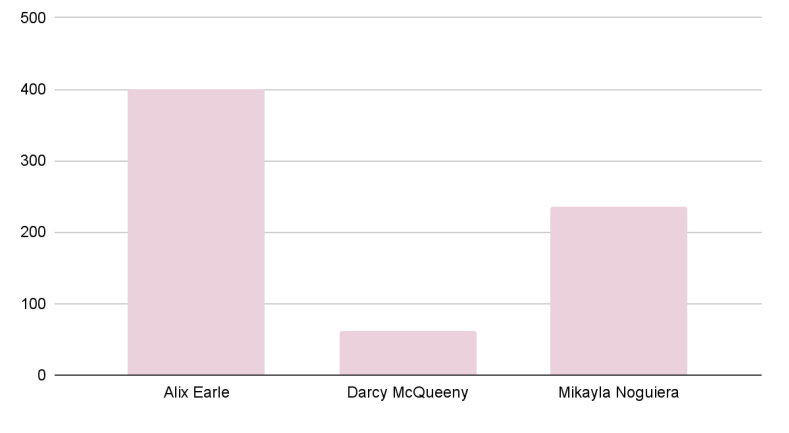
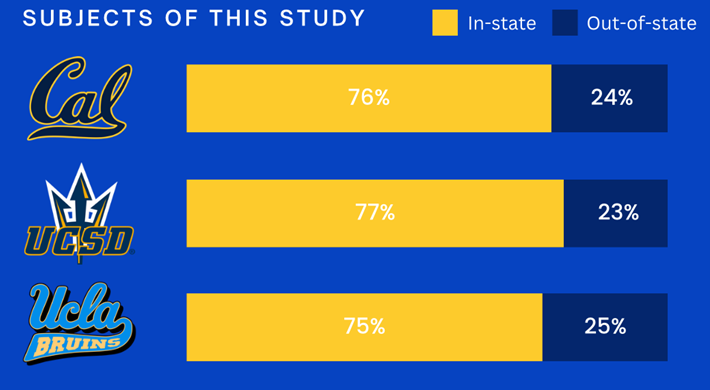
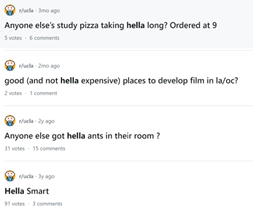
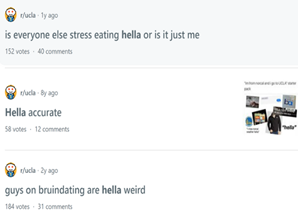
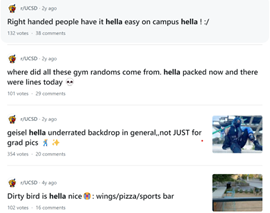
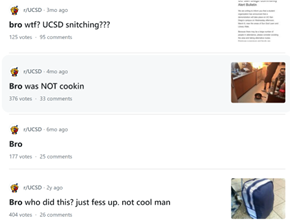
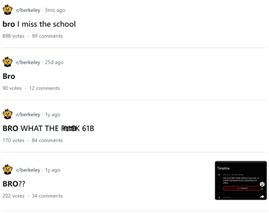
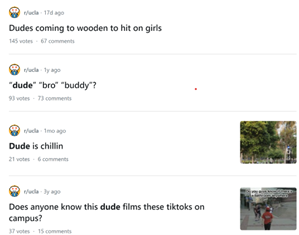
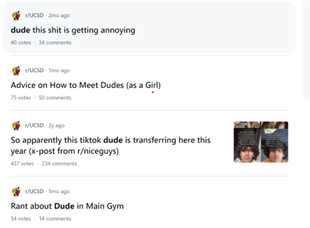
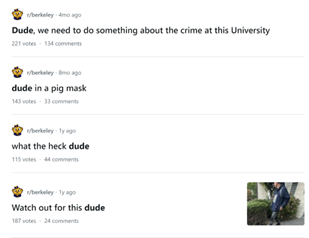
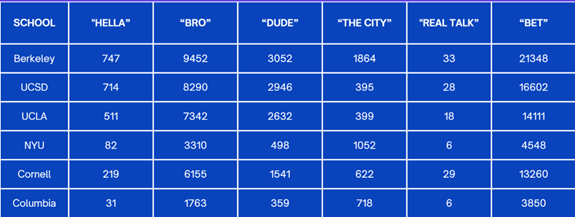
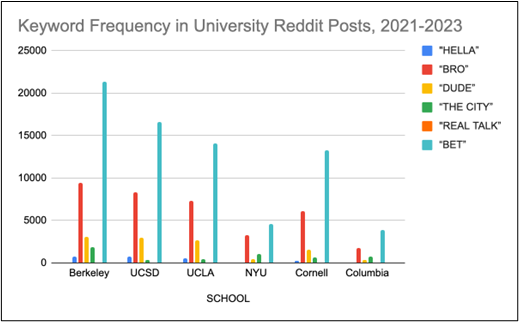
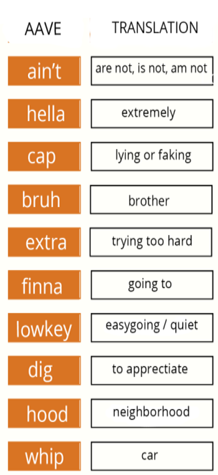
Introduction and Background As aspiring sociolinguists, we want to learn more about how different cultures can affect slang within our own communities and thus, affect their way of speech. More specifically, how do students at different universities use slang, and what are the implications of this language? University culture is unique and cultivates an environment of relatability and unity. Language and communication play a big role in this culture, and with the rise of social media platforms, we decided to dive into a platform largely used by university students in order to analyze raw conversations between college students within a university. More specifically, we analyzed California university slang versus New York university slang. Reddit is a great place to analyze linguistic features and speech of people across the United States and how each geographical place affects their slang. Reddit is a social networking platform that was established in 2005 (Semrush, 2024). In addition, Reddit is divided into communities called “subreddits,” where people can interact and contribute with each other comfortably in their respective community. These subreddits generally consist of people with the same interests. In this case, we examined Reddit communities for universities, meaning most users go to the same college or university. Within these subreddits, users relate to one another using university- and state-specific slang. New Yorkers have a diverse immigrant population and fast-paced urban lifestyle. They also tend to partake less in small talk and more in longer, conversational speeches (Allen 2023). In those conversations, there are a couple of common terms, such as “real talk” (attention grabber), “the city” (refers to Manhattan), and “Stoop” (steps outside of an apartment). Conversely, Californian slang and language reflect tech and entertainment culture, primarily because of the Los Angeles area or most of the tech companies that reside in San Francisco. In addition, Californians tend to use relaxed jargon and more informal speech patterns (Bucholtz, n.d). Some of the common terms they used are: “hella” (very much), “like” (mostly as a filler word), and “dank” (excellent). Based on these backgrounds we posed the questions: How do linguistic markers, especially slang, differ in New York vs. California universities on Reddit? How do regional, cultural, and social influences affect language? Do in-state versus out-of-state student populations affect the use of slang within university subreddits? Overall, this research study examines the different linguistic features of the California and New York universities. We aim to show that these variations reflect the unique social and cultural aspects of each region, highlighting how language usage serves as a marker of regional identity in digital communication. Methods Earlier this year, a Reddit user named u/Watchful1 compiled data collected by other users, u/pushshift and u/raiderbdev, on posts and comments from Reddit between 2005 and 2023. We isolated six subreddits relevant to our study. We used scripts from Watchful1’s PushshiftDumps Github repository to count the occurrences of specific keywords in each subreddit from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2023. For web scraping, we used Python libraries like BeautifulSoup and PRAW to extract data from Reddit communities associated with universities in New York and California. We selected subreddits based on criteria such as member count, post frequency, and relevance to student life, focusing on threads that accurately represented each region’s schools. We aimed to collect a diverse sample of posts and comments from each selected subreddit, ensuring representation across various topics, time periods, and user demographics. In cases where automated methods might miss nuances, human annotators manually reviewed and supplemented the analysis. We also prioritized ethical considerations by anonymizing or aggregating data to protect user confidentiality, ensuring compliance with Reddit’s terms of service and data usage guidelines. We also conducted thorough reliability checks to ensure the quality and accuracy of our data and analysis results. In addition and most importantly, we intended to select a few universities because it would be time consuming and difficult to do all of the subreddits for California and New York universities. Thus, we chose to focus on a few universities in each state with the most active subreddits and number of reddit community members. Finally, we maintained detailed internal documentation of our data collection process, including sources, sampling methods, and any preprocessing steps applied to the data. Results and Analysis First, it is important to note the distribution of in-state versus out-of-state students. We collected this data from the universities, and the distribution is shown below. After using our methods of analyzing Californian and New York universities’ slang, we found that college students in California use the word “hella” the most at UCLA, even more than in UCSD and UCB, although it is still very prevalent in all three California schools. “Hella” means “there’s a lot of __.” The reasoning for the frequency is due to the recency of each university subreddits; the longer the comments were posted would not be helpful in determining today’s society’s slang. For instance, most of UCLA comments were from 3 to 6 months ago while UCSD and UCB’s comments were from 2-4 years ago, which is a significantly longer time. In addition, “hella” is “highly expressive [and] often” will destroy the gravity of a formal statement (Hummon 1994). Common examples of the use of “hella” are shown below: Secondly, we also found that college students among UCLA, UCB, and UCSD primarily frequent the slang “bro.” The comments we have found were not from too long ago, ranging from 4-9 months. Since these comments were recent, we can say that the accuracy of California universities students saying “bro” is likely. Moreover, we can also say the same for “dudes” because of how recent it is. Students say “bro” and “dudes” because omitting large chunks of a particular sentence or word helps the speaker say what they mean. In other words, it might be difficult for the speaker to say “brother,” a longer version of “bro.” Including the second half of the word loses the surrounding, cultural meaning of the sentence, i.e, “bro was not cooking” is not the same as “brother was not cooking” in terms of today’s societal norms. This shows how even slang has its own set of unspoken “rules” that must be followed to maintain a level of informality befitting more casual contexts. Shortening words seems to be a trend for making phrases more casual, and this could perhaps be due to how it allows a speaker to convey more in a shorter amount of time, as well as an implied mutual understanding between the speaker and listener that they understand the true meaning despite it being shortened, similar to a secret code. This could also be why slang usage is so prevalent nowadays, as everyone sees it as cool or modern to be part of a community that understands this secret code, the language of slang. Eventually, slang will become “accepted as equivalent to their unabbreviated and original forms” (Gordon 2020). Even though some slang words like “hella” are not widely spoken in other universities, it will be useful in the near future for linguistic research. More examples of “bro” and “dudes” shown below: Moving on to the New York universities, we found that “the city” is used more frequently at NYU and Columbia than in Cornell. “The city” means Manhattan, and college students from NYU and Columbia use it more because they are closer to Manhattan than Cornell. However, another slang term, “real talk” (used as an attention grabber), is more common in Cornell than the two other universities. In addition, the most common frequency slang in Cornell is “bet,” meaning you are either asking the person to put money on your statement or an affirmative ‘yes.’ This is also slightly common in NYU and Columbia. Moreover, what we found interesting is that the subreddit comments of these NY slangs are from 3-4 years ago. However, when we tried to fact-check this with our current methodology using a Python script, we found that the slang “bet” is used by all universities from the west to east coast. For example, there are roughly 21,348 “bet” usages at UC Berkeley, followed by UCSD, while there are 9,452 slang “bro” at UCB. We also found that “real talk” is less common in all universities. Here is the common occurrence table including data analyzed by the Python script between January 1, 2021 and December 31, 2023: Discussion After analyzing the linguistic features of California and New York, especially slang, we can safely say that slang words that would be considered be California slang are used heavily within Californian universities’ subreddits. This seems to have a direct correlation to the number of in-state students, unlike New York universities. We also observed several frequent uses of the same terms — “hella,” “bro,” and “bet” — across the Californian universities. In addition, we can say that college students who mainly grew up in an active social culture will most likely be accustomed to the slang and jargon around them. Moreover, as for New York universities in their own respective subreddits, they use less frequent jargon and slang. Although still present, this seems to have a direct correlation with the amount of out-of-state students in each NY university, as fewer students grew up immersed in the New York culture and thus, are less likely to be accustomed to the city language influenced by the city’s culture. Our research study contributes to a larger phenomenon in different ways. Firstly, by analyzing linguistic patterns in Reddit communities, the study sheds light on the social dynamics and communication styles within university-affiliated online spaces. This understanding can inform community management strategies and facilitate more effective online interactions. Secondly, our findings contribute to educational research by highlighting the role of language in shaping online discourse within academic communities. Sociolinguistic studies can benefit from a deeper understanding of how language reflects societal norms and values in digital environments. Lastly, we can leverage insights from this research to develop more targeted and engaging digital communication strategies tailored to specific regional audiences. Understanding linguistic preferences and cultural references can enhance the effectiveness of online marketing and outreach efforts. For example, we can use common slang and jargon, such as using a lot of “bros” or “dudes,” in a men’s marketing campaign and planning how it will raise awareness. Conclusion Ultimately, each university and its own subreddit cultivates a community that is centered around shared and common experiences. These experiences can create and preserve slang and jargon that students feel comfortable using to express themselves. There is also a prevalent influence of regional culture on language and slang used by Redditors across the country, as shown by the different terms most used in California and New York. Even though students may move out of state to attend college, they will bring their own slang used by their hometown communities with them, rather than immediately assimilating into the language used in their new community. Overall, language stands as a symbol of hope and it is used so that other students accept and recognize one another as part of the same community. References Allen, I. L. (2023). The city in slang: New York Life and popular speech. Oxford University Press. Bucholtz, M. (n.d.). Chapter 29- Word Up: Social Meanings of Slang in California Youth Culture. In A Cultural Approach to Interpersonal Communication: Essential Readings. essay. Haas, C., Takayoshi, P., Carr, B., Hudson, K., & Pollock, R. (2011). Young People’s Everyday Literacies: The Language Features of Instant Messaging. Research in the Teaching of English, 45(4), 378–404. http://www.jstor.org/stable/23050580. Hummon, D. M. (1994). College Slang Revisited: Language, Culture, and Undergraduate Life. The Journal of Higher Education, 65(1), 75–98. https://doi.org/10.2307/2943878. Labov, T. (1992). Social and Language Boundaries among Adolescents. American Speech, 67(4), 339–366. https://doi.org/10.2307/455845. Roth‐Gordon, J. (2020). Language and creativity: Slang. The International Encyclopedia of Linguistic Anthropology, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118786093.iela0192. Saha, Koustuv & Choudhury, Munmun. (2021). Assessing the mental health of college students by leveraging social media data. XRDS: Crossroads, The ACM Magazine for Students. 28. 54-58. 10.1145/3481834. “Top Websites in Worldwide (All Industries).” Semrush, www.semrush.com/trending-websites/global/all. Accessed 20 May 2024.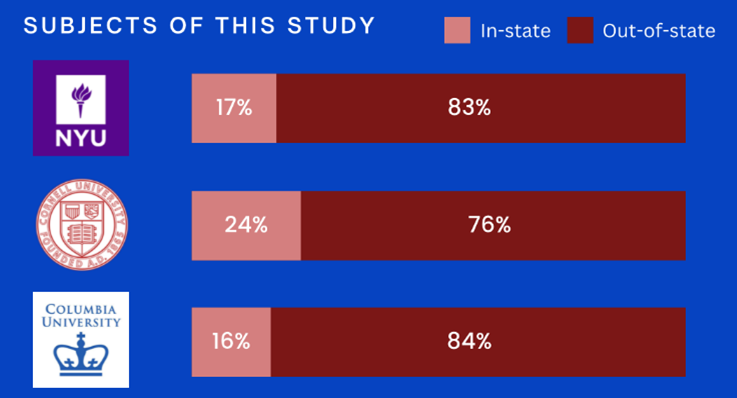



 Methods
Methods