CODE SWITCHING!: A phenomenon among bilinguals and its deeper role in identity formation
Leon Kaprielian, Octavio Santana, Sahil Sadiq
In an era marked by globalization and multiculturalism, the phenomenon of code-switching has emerged as a crucial aspect of language dynamics and identity formation among bilinguals. The complexities of code-switching, its popularity, and its deeper ramifications for people navigating many linguistic and cultural domains are explored in this research. We examine how code-switching is used in immigrant communities as a tool for social interaction, identity negotiation, and effective communication through a multidisciplinary lens that takes into account linguistic, cognitive, cultural, and social factors. Based on naturalistic observations and interviews with Farsi, Spanish, and Arabic bilingual speakers, we investigate the complex patterns of code-switching in various age groups and social circumstances. Our research shows that code-switching is a reflection of complex social dynamics, such as social hierarchy, respect for elders, and the maintenance of cultural identity, rather than just a linguistic issue. This study emphasizes how crucial it is to comprehend language practices in a multicultural and globalized world by shedding light on the significance of code-switching in forming people’s identities and social structures.

Introduction
Code-switching was formerly thought to be a linguistic oddity, but research has since shown that it is a regular aspect of language use. It illustrates the intricate interactions between linguistic, cognitive, cultural, and social elements that influence social interaction and identity formation. Determining the mechanics of bilingualism and multiculturalism, illuminating the complex ways language influences social structures and human interaction requires an understanding of code-switching.
What is code-switching?!
Code-switching is the fluid transition between two or more languages in a single discourse and is an effective communication and identity-negotiation technique for immigrant communities. Moreover, it is a great way for individuals to build rapport with members who speak the same language. The informal aspect of this will lead to a higher frequency of code-switching and a willingness to express one’s cultural identity, as opposed to a formal environment. In terms of the types of code-switching, it comes in three forms, intrasentential, intersentential, and tag switching.

New to code-switching? Here are the methods we used and how you can do it too!
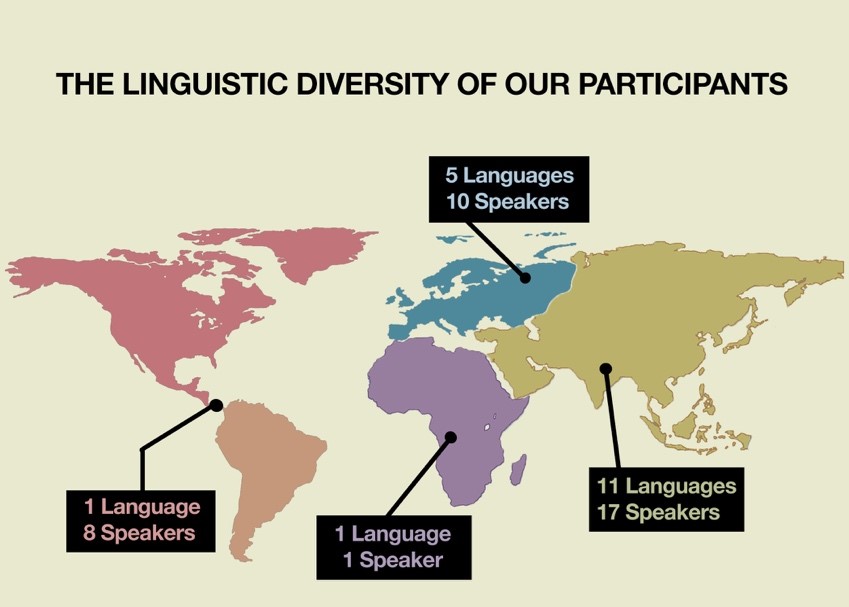
In this post, we’ll discuss methods used for collecting the data that include studying code-switching in a natural environment, and with the authentic use of language by bilingual or multilingual speakers. One of the ways we are going to collect the data is by naturalistic observation. This involves observing naturally occurring conversations in its most pure form, which is essentially the most authentic form of data collection by bilingual and multilingual individuals. To give an extra set of diversity and universality in this regard, there are going to be 3 languages discussed: Farsi, Spanish, and Arabic.
Results
Farsi (Dari)
There is a difference in the amount of code-switching in regards to whether a Gen Z immigrant is speaking with their own age group or with elders. In Farsi, when one is speaking with elders, it occurs at a much higher frequency and it is more on the “Intersentential” level. The reasoning is due to 1) Innate understanding that the elders prefer the native language 2) The elders’ proficiency in English is not as advanced.
In regards to when the Gen Z bilinguals speak amongst themselves, there is more English spoken, and during the naturalistic observation, the ratio was 80% English to 20% Farsi. When the code-switching did occur, unlike with the elders, which (was usually intersentential), it was intrasentential and tag-switching.
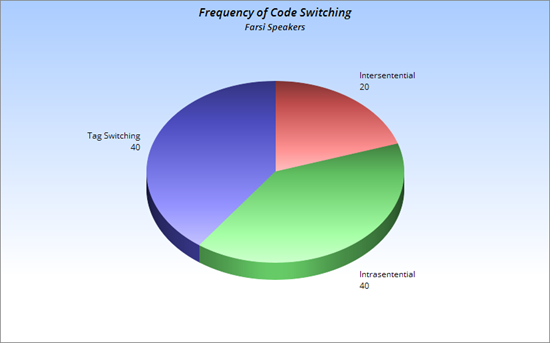
Lastly, although naturalistic observation was the main method to keep the results as organic as possible, interviews with 2 of the Gen Z members were held to articulate and discuss potential biases and limitations. One of the members (20 years old) said the code-switching just happened naturally without much thought. The eldest in the observation (29) said that he does it naturally but also consciously, either due to the fact certain words in Farsi seem articulated better, and also to build rapport with the group culturally, which ties into our main thesis that the phenomenon of code-switching is usually intimately linked to one’s cultural identity.
Spanish
To continue, Spanish and English bilingual speakers tend to gravitate towards an unofficial language, Spanglish. This is when English and Spanish are combined in conversation. Spanglish is a form of code-switching, setting the foundations for forming one’s identity, while simultaneously maintaining their culture.
The method used was a naturalistic observation of a phone call between a bilingual speaker and their parents. They answered the phone in English, just like they do with friends and people of the same age. Spanish was used rarely and the language used had no link to what type of person they were speaking to. The phone then got passed to the speaker’s grandma, and that is when the bilingual speaker started speaking only Spanish. The Spanish the speaker used were easy to decipher that they were speaking to someone of an older age because words like “usted”(you) and “mande”(excuse me) were used. These are formal words and are used when speaking to strangers or elders.
After tallying up the number of formal words used in the phone call, all of them came when speaking Spanish, except one coming from English. The research shows that code-switching can occur within a family and also how a change of language is made to show respect. The same goal could not be achieved with English, since Spanish has an emphasis on formal speaking, causing the speaker to have a complete shift of identity when code-switching.
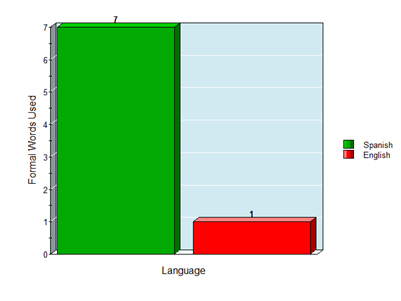
Language is inherently tied to respect when concerning age, class, and gender in Spanish, showing how language can shape the way one thinks.
Arabic
Bilingual Arabic speakers are more likely to use religious jargon (inshallah, mashallah) when interacting with parents and other elders. When speaking to friends, siblings, and cousins they are most likely to speak a 70/30 mix of English and Arabic in contrast to a 20/80 mix when speaking to Elders. Another important consideration is the intonations and accents used for certain words when speaking each language. Because Arabic and English have a very different set of sounds, the same word can be pronounced differently depending on the spoken language. For example, most native speakers of both English and Arabic know that Pepsi – with a p – is the correct pronunciation of the soda, however, they will still pronounce it like Bebsi with a b sound when speaking Arabic. This is done to signal that the speaker is native in Arabic and is part of the Society of native Arabic speakers who do not use the P sound.
Discussion and Conclusions
All three languages investigated truly show just how intricate and complex languages are, especially when it comes to code-switching. Our research shows how code-switching plays an extremely crucial role in forming one’s identity and how it goes beyond just language. It reflects social dynamics like social status, respect for elders, and cultural identity preservation. Our study contributes to the gap of knowledge of understanding how native languages travel down from generation to generation in immigrant families in America, and how code-switching shapes who we are and the social groups we belong to.
References
Albirini, A. (2011). The sociolinguistic functions of codeswitching between Standard Arabic and Dialectal Arabic. Language in society, 40(5), 537-562.
Heller, M. (2020). Code-switching and the politics of language. In The bilingualism reader (pp. 163-176). Routledge.
Kachramanian, C. (2021). Bilingual Interactions: An Investigation into Code-switching and Its Purposes among Armenian-Dutch Bilinguals.
Klavans, J. L. (1985). The syntax of code-switching: Spanish and English. In Proceedings of the Linguistic Symposium on Romance Languages (Vol. 14, pp. 213-231). Amsterdam: Benjamins.
Martin-Jones, M. (1995). Code-switching in the classroom: Two decades of research. One speaker, two languages: Cross-disciplinary perspectives on code-switching, 90-111.
Myers‐Scotton, C. (2017). Code‐switching. The handbook of sociolinguistics, 217-237.