The Experiences of Non-Native English Speakers at UCLA
Christina Oghlian, Cia Evangelio, Nina Esteghlal, Rikuto Kawada, Yuka Tanaka
As a native speaker of a language, we never really stop to think about the experiences and challenges of those who are not native speakers. It is especially difficult for those who are studying in a foreign country where almost everyone is fluent in a different language than them. We decided to research what challenges international students face in order to gain a greater understanding of their experiences as non-native English speakers at an American university. In addition, we want to use the results of our findings to understand what resources are available for international students who are not English-proficient.
We conducted our research by interviewing 10 international students attending UCLA, 5 of which were male and 5 of which were female, about their English academic proficiency levels and their experiences in various social settings as non-native speakers. By creating more spaces where international students can meet one another or consult with fluent English speakers about difficulties they might have with the language, educational institutions can help their international students feel more safe and comfortable in both academic and social settings.
Introduction
Think about yourself living in other countries where people do not speak your native language. What would you feel, and what difficulties would you face? This curiosity makes us want to study how each international student struggles to live in other countries. We focus on the linguistic, social, and mental challenges that international students face during their study abroad experiences. Our research question is: “How does international students’ English proficiency affect their personal life to be fulfilling while they are studying abroad, and what are the difficulties for international students to achieve their ideal life in new countries?” We hypothesize that international students with higher proficiency in speaking English have more opportunities to socialize in groups. On the other hand, international students who have lower English proficiency will face more difficulties in socialization and having an awareness of their speaking English, increasing their anxieties while they are speaking English to native speakers.
Background
International students face new challenges in a new country. There can be many reasons and situations, such as the language barrier, socialization, and mental condition. Those challenges have a huge negative impact on international students in terms of their studying or speaking English. Many international students are willing to enhance their speaking skills and engage in new social interactions, such as engaging in conversation, making new friends, and so on, in the new countries they go to (Bernhard and Gregory, 2017). Depending on the individual international students, there are differences in these achievements to be different because their English proficiency will be affected.
The linguistic barrier can make people feel they are not in the conversation while people are speaking English because they cannot understand and speak out while people are using English. This can make international students feel socially excluded because of the differences in their English ability (Hilt, 2016). In addition, linguistic barriers are affecting not only the social life of international students but also their mental awareness of their English ability in many ways. While international students feel they are not good enough at speaking English, it can affect their feelings of anxiety (Idrissi, 2022). Moreover, the linguistic barrier can also affect international students’ confidence in speaking (Iris and Lopez, 2014). Therefore, English proficiency has a huge impact on the interactions with international students, their social lives, and their awareness of anxiety.
Methods
For our research study, we aim to interview 10 international UCLA students between the ages of 18-25. Out of the 10 international students, we will specifically interview 5 males and 5 females. Our research will examine how these international students face difficulties when they are speaking English to a native English speaker. Before the interview, the students will complete a Google form asking a couple of questions about their demographics, including identity, where they are from, previous schools they have attended, and for how long they have been attending UCLA. After completing the Google form, each participant will be notified with a follow-up interview and be asked questions based on their familiarity with English. The interviews will take approximately 30 minutes, and we will ask questions related to their knowledge of English, such as, “How comfortable are you speaking English”, “What is the most complicated part about speaking the English language”, “ How comfortable are you when slang is being used in conversation”, and “What linguistic features do you pay attention to when speaking with native speakers”. Based on the interview answers, we will analyze them to see what international students struggle with and which areas of linguistics they have difficulty understanding the most. We especially want to understand how international students have a difficult time with their English ability in social situations and mental interaction.
Results and Analysis
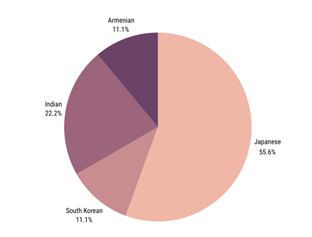
The results that we have found are quite intriguing. We conducted a total of nine interviews and created graphs to represent our findings. As represented on the charts, the demographic of our participants is a majority of Japanese participants followed by Indian, South Korean, and Armenian, as shown in Figure 1.
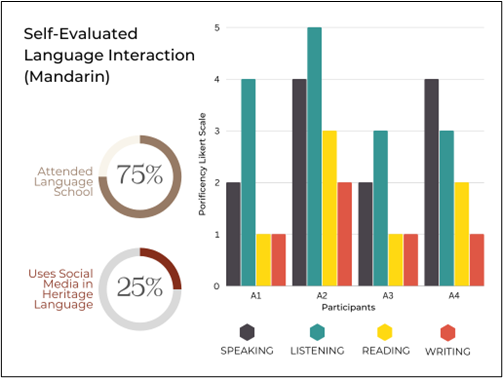
A large majority of the participants were exposed to English in high school– whether that be that they went to an international school or they had an integrative English course as represented through Figure 2.
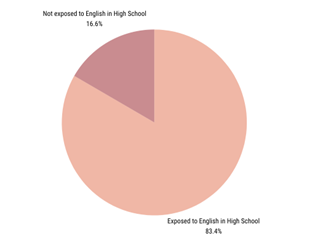
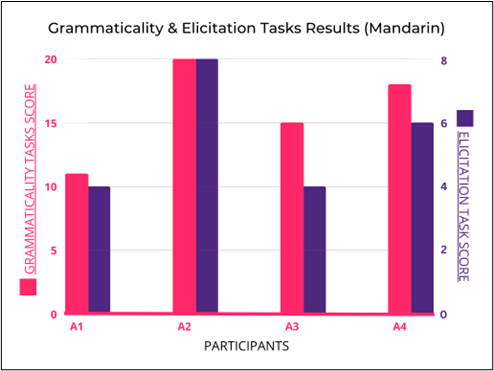
While conducting our research, we realized it was only fair that we separate international students from what was shown in Figure 2. Out of those international students that were exposed to English in high school, Figure 3 represents what they found the most difficult when participating in conversation with native English speakers.
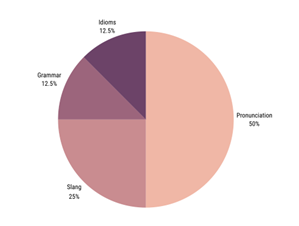
On the other hand, Figure 4 shows what international students that have lesser English proficiency struggle with. Interestingly, both international students with strong English proficiency and students with lower English proficiency are most conscious about pronunciation.
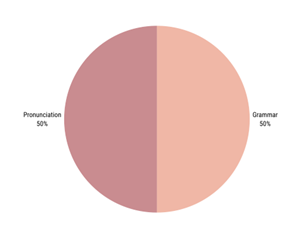
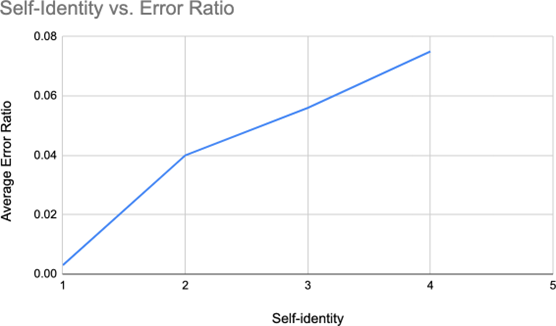
The results show that the international students that have a strong English-speaking background are most likely to feel comfortable speaking English to individuals, and group settings however, international students with no English background feel less comfortable. International students have more difficulty grasping English morphological and syntactic structures due to the complicated grammatical structures that are used in academic settings. The use of slang terms and pop culture usually in social and school settings often would give international students confusion. Most international students mentioned how they struggled understanding slang terms and pop culture and that they are still learning.
Discussion and Conclusions
Previous studies have shown that the ability to speak English is highly related to one’s involvement with the surrounding environment in which he or she grew up. The results show that international students who received an academic English education before entering university are almost as confident and comfortable with their English skills as native English speakers, whereas international students who did not receive much English education before entering university are a little more hesitant to speak English. As our research indicates, they may feel anxious or difficult to speak depending on their proficiency in English and may feel that they do not belong in that group.
Moreover, our study allows us to speculate that difficulties in grasping specific and unique syntactic structures, such as pop culture references, may have an impact on the minds and bodies of international students. While it is difficult to draw conclusions, this phenomenon may be true for many international students who did not receive much English education before college. Proficiency in English is a necessary skill for international students to adapt to social life, but confusion often arises when slang and pop culture references are mixed in. Therefore, it could be argued that international students hang out with other international students to avoid being excluded because of differences in fluency or proficiency that they do not possess compared to native English speakers. This research can be applied to various university communication settings to help understand how to properly engage with international students and what type of environment is most effective for language learning.
References
Alkhammash, R. (2022). Processing figurative language: Evidence from native and non-native speakers of English. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1057662–1057662. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.105766
Drljaca Margic, B. (2017). Communication courtesy or condescension? Linguistic accommodation of native to non-native speakers of English. Journal of English as a Lingua Franca, 6(1), 29–55. https://doi.org/10.1515/jelf-2017-0006
Halic, O., Greenberg, K. H., & Paulus, T. M. (2009). Language and Academic Identity: A study of the experiences of Non-Native English speaking international students. International Education, 38(2), 73–93.
Hilt, L. T. (2016). Education without a shared language: Dynamics of inclusion and exclusion in Norwegian introductory classes for newly arrived minority language students. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 21(6), 585–601. https://doi.org/10.1080/13603116.2016.1223179
Idrissi, O. (2022). Anxiety as a psychological barrier to students’ speaking fluency: IELTS as a case study. International Journal of Linguistics, Literature and Translation, 5(12), 111–120. https://doi.org/10.32996/ijllt.2022.5.12.14
Jessen, A., Festman, J., Boxell, O., & Felser, C. (2017). Native and Non-native Speakers’ Brain Responses to Filled Indirect Object Gaps. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 46(5), 1319–1338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-017-9496-9
Lopez, I. Y., & Bui, N. H. (2014). Acculturation and linguistic factors on international students’ self-esteem and language confidence. Journal of International Students, 4(4), 314–329. https://doi.org/10.32674/jis.v4i4.451
Streitwieser, B. T., & Light, G. J. (2017). Student conceptions of international experience in the study abroad context. Higher Education, 75(3), 471–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-017-0150-0
Yu, X., & Peters, B. (2019). Let All Voices Be Heard!: Exploring International Students’ Communication Challenges in the Internationalized Classroom. Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies in Education, 8(1), 107–116. https://doi.org/10.32674/jise.v8i1.1080
Cross-referencing relevant info: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=na04NxGZuKU