Formality in the UCLA Community: Communication and Self-Expression in the Digital Age
Online communication has undoubtedly brought on more opportunities for misunderstanding. However, the use of linguistic elements such as internet slang and emojis represent the myriad ways that humans expand our linguistic toolbox. Through our research, collected through online surveys and interviews with several members of the UCLA community, we found that formality is shaped by many complex factors, including similarity or difference in age, gender, and power dynamics between interlocutors. The prevalence of concepts such as mirroring suggests that maintaining appropriate levels of formality in these evolving communication mediums is an intuitive process which calls upon participants to be more attentive and creative communicators. Additionally, we found that these processes reveal that, although traditional notions of formality and politeness continue to shape our ways of interacting, the very definitions of these concepts are ever-changing.
Introduction
The rapid evolution of virtual communication technology is changing the way language is used, allowing interlocutors to use a vast range of tools such as visual elements and online slang, changing the way we come to know language. This results in the creation of a new set of language practices specific to online interactions. Naomi Baron delves into the pervasive influence of digital communication has led to a shift in language structure from traditional, standardized language to one that is more fluid and de-standardized (Baron, 2012), which is what we are aiming to look at. In our research, we investigate the nuances of formality and politeness through surveys and interviews with members of the UCLA community, allowing them to explain the nuances of their own communication habits – calling into question how concepts of formality and politeness may change over time.
Kadar and Mills discuss this in their work where they delve into politeness theory; culture is sometimes treated as rigid rules, potentially portraying individuals as passive recipients. The alternative perspective views culture as “embodied practices,” emphasizing the dynamic manifestations in individuals’ daily lives. (Kader & Mills, 2011.) We seek to understand how UCLA students navigate the world of virtual communication in an academic setting. Furthermore, we aim to gain a stronger grasp on our focus group’s subjective views regarding notions of formality and politeness. Our hypothesis suggests that UCLA students adopt more formal language when communicating with authority figures, such as older individuals or those in higher positions. This implies a tendency to avoid informal tools like slang or emojis. Despite evolving social norms, traditional notions of formality and politeness continue to influence how students speak.
Our focus group, members of the UCLA community, depend heavily on digital mediums for most interactions. When it comes to messaging, emails, and social media, students’ attitudes toward formality have a large impact on their interactions. In essence, our research looks at the variety of linguistic behaviors at UCLA, the opportunities and challenges presented by digital communication, and the effects these may have on academic connections and social relationships.
Methods
We employed a combination of qualitative and quantitative methodologies to gather data across the diverse sprawl of the UCLA community. This included participants ranging from professors and students to teaching assistants and other faculty members. The data collection process was executed through in-person interviews as well as a Google Form Survey. Our dataset consisted of 10 in-person interviews and 42 survey responses, providing a comprehensive basis for an in-depth analysis of participant responses.
The in-person interviews were approximately 15-30 minutes, while the 8-question survey was designed with efficient qualitative analysis in mind. Furthermore, the in-person interviews consisted of open-ended queries addressing a range of themes related to informal vs. formal communication and touched on aspects including abbreviations, emojis, non-verbal cues, body language, tone, familiarity, time sensitivity, and slang. The online survey consisted of predetermined response options, whereas the interviews were designed to facilitate open responses. After data collection, interview transcriptions were analyzed to identify patterns of similarity and difference between the interviews and the survey responses.
Throughout the data acquisition phase, our project encountered a few challenges. One notable limitation: our data exclusively relied on self-reported behaviors, perhaps resulting in a lack of impartiality that an observation-based method, such as conversational analysis, may have provided. (Meredith, 2020.) Moreover, the authenticity of responses generated from both interviews and the survey responses were contingent upon the honesty of the interviewee or respondent. However, the online survey was anonymous, which may have generated more genuine results from the respondents, as the perceived risk of judgment is mitigated. Lastly, the data was thoroughly analyzed to identify patterns of evidence that would either support or deny our hypothesis.
Results and Analysis
The findings suggest that in most forms of communication, people tend to mirror the habits of those they interact with. There was a tendency to adapt levels of formality based on context, such as being more formal in professional or educational settings, and less formal in casual conversations or on social media. This was also influenced by the medium of communication as well as the relationship with the individual, with more formal language used in emails and with superiors, while informal language is reserved for friends or family. Many interviewees stated that they often “mirror,” or match the communication style of the person they are addressing. This could involve adopting similar speech patterns, gestures, or even body language. Furthermore, “matching energy” involves adjusting one’s approach, such as using emojis or punctuation, to align with the other person’s formality level.
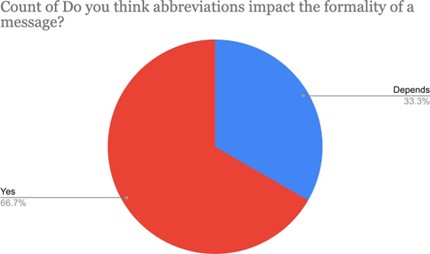
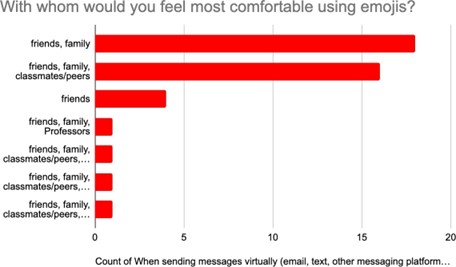
Emojis and abbreviations are more common in informal settings and less in professional contexts. Frequency of communication and level of familiarity also influence language choice, with increased informal language aligning with an increase in familiarity. Our findings suggest that non-verbal cues such as body language and eye contact allow for easier communication because they create a “live feedback loop,” a term used by several interviewees. A “live feedback loop” occurs when one concentrates on another’s non-verbal cues during an interaction as a signal for understanding their unspoken thoughts and general disposition. This represents a certain level of intuitiveness and a strong attention to detail. In online communication, where non-verbal cues are absent, looking for these cues in word choice. Individuals tend to carefully proofread emails, especially those addressed to professors. In time-sensitive scenarios, certain interviewees default to casual language, while others prefer formal expressions. Additionally, the flexibility to switch between formal and informal language within the same conversation is deemed appropriate depending on the context and relationship with the interlocutor.
We hypothesized that UCLA students adjust the formality of their linguistic patterns when interacting with individuals of superior authority, such as older individuals or those in higher positions. Our findings indicated that people tend to mirror the communication habits of those they engage with, adjusting their level of formality based on context and relationship dynamics. In professional or educational settings, where a higher degree of formality is expected, individuals typically employ formal language. In casual conversations or on social media, a more relaxed tone is used. The utilization of emojis and abbreviations, common in informal settings, diminishes in professional contexts, reflecting the hypothesis that normative ideas of formality continue to influence linguistic behaviors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our research on the formality of linguistic patterns in virtual communication among UCLA students and faculty reveals that individuals adapt their language based on the context, medium, and relationship with the interlocutor. The findings confirm our hypothesis that students increase the formality of their linguistic patterns when communicating with authority figures, such as older individuals or those in higher positions. Emojis and abbreviations, common in informal settings, are used less frequently in professional contexts, indicating a clear distinction in language use based on the perceived formality of the situation. The concept of a “live feedback loop” in face-to-face interactions aids in understanding and adjusting communication, a feature lacking in online exchanges, where careful word choice and proofreading become essential.
Overall, this research provides valuable insights into the dynamics of virtual communication among UCLA students, emphasizing the influence of formality and politeness in linguistic patterns. Furthermore, our results reveal the delicate cooperation and reciprocity which online communication demands from its participants. Future studies could explore the impact of cultural differences on communication styles and the evolving nature of language in the digital age.
References
Baron, Naomi S., (2012). The impact of electronically-mediated communication on language standards and style’, in Terttu Nevalainen, and Elizabeth Closs Traugott (eds), The Oxford Handbook of the History of English, Oxford Academic, 6
Lorenzo-Dus, N., & Bou-Franch, P. (2013). A Cross-Cultural Investigation of Email Communication in Peninsular Spanish and British English: The Role of (In)Formality and (In)Directness. Pragmatics and Society, 4(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1075/ps.4.1.01lor
Kádár, D. Z., & Mills, S. (2011). Politeness in East Asia: Chapter 2, “Politeness and culture” Cambridge University Press
O’Reilly-Shah, V. N., Lynde, G. C., & Jabaley, C. S. (2018). Is it time to start using the emoji in biomedical literature? BMJ: British Medical Journal, 363. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26964183
Meredith, Joanne. (2020). Conversation analysis, cyberpsychology, and online interaction. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, Volume 14, Issue 5.