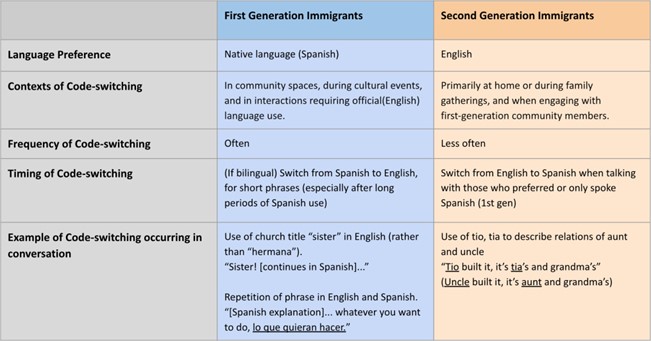
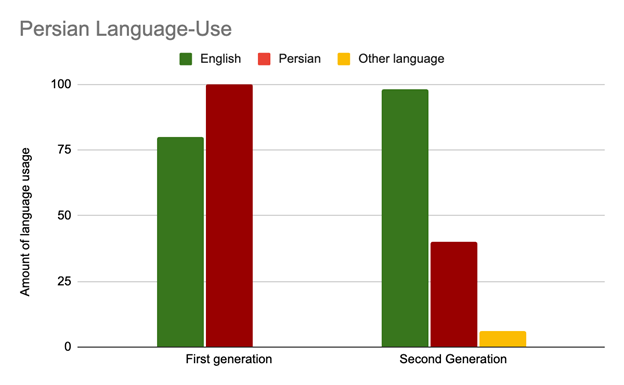
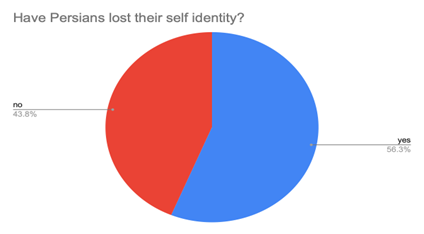
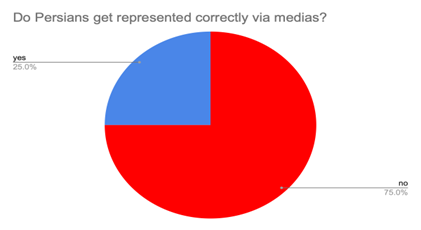
Friendships For the Mono- and Bi-Lingual College Student: Does The Language You Speak Make A Difference in How You Make Friends?
In the course of our research, we endeavored to examine the difference in the social life of UCLA college students, their capacity to make friends, and satisfy their need for social support with fellow students based on their status as a monolingual or bilingual speaker of English. Drawing on support from previous research dealing with different student populations, we concluded that the way bilingual students are treated and form communities is different from the way monolinguals do, whether because of “othering” by speakers who did not understand their language or culture or because they sought out connections with those who shared their ethnic or linguistic ties. It was almost universal in our interviews where bilingual speakers had a bias towards others who spoke their non-English language, and many of the monolinguals admitted to preferring the company of those who shared their language and culture. Not every speaker who our team interviewed had an exactly identical experience, however- none of our bilingual speakers derived from the same culture or spoke the same language- and there were a few interesting perspectives and outliers.
Introduction
In the course of their education, every single college student is faced with the point where they realize that they are now, effectively, adults and they are now- potentially for the first time- on their own. Many freshmen entering into university are inbound to a new city, a new county, new state, or even an entirely new country. The locale, culture, and people are all different than where they are originally from.
This gap in culture (and sometimes even language) and the responsibilities endowed by college life can make it difficult to make friends in a new place– but it is also extremely pivotal for mental and social well being to make social connections, given the loneliness of being far from home and isolation from the people one knows.
Researching into how students- particularly bilingual students- construct their new friendships is invaluable for anyone incoming to university. Using UCLA students as a representative example, we can explore some of the insights of students navigating their new social landscape. Most specifically, we want to see how- and if- monolinguals and bilinguals differ when it comes to trying to form friendships, and why.

Methods
We began our research on how bilinguals and monolinguals in college differ in making friends and their differing level of social satisfaction in the college environment by consulting various published literature on the subject, but intended to do our own interviews and surveys to see if anecdotal evidence matched the broader scientific findings. Across many different papers- from bilingual college students of Chinese or Latinx descent all the way to the bias of young monolinguals from 4 to 6 years of age- we found a fairly consistent trend: bilinguals liked grouping with other bilinguals (specifically ones of their own culture and language) and monolinguals tended a slight cognitive bias (conscious or otherwise) towards other grouping with monolinguals.
When we had seen the literature’s assessment of college friendships by bilinguals, we formed our hypothesis about the difference: that bilinguals tended to find it easier to make friends with bilinguals from their culture and that monolinguals tended either to “not care” or stick with monolinguals. We also sought out whether being bilingual was particularly helpful in making social connections compared to monolinguals, and other potential social benefits of bilingualism in a predominantly English-controlled American college environment. With our research question and secondary and tertiary objectives in mind, we put our theories and the broader literature to the test through qualitative and quantitative surveys and interviews.
Results
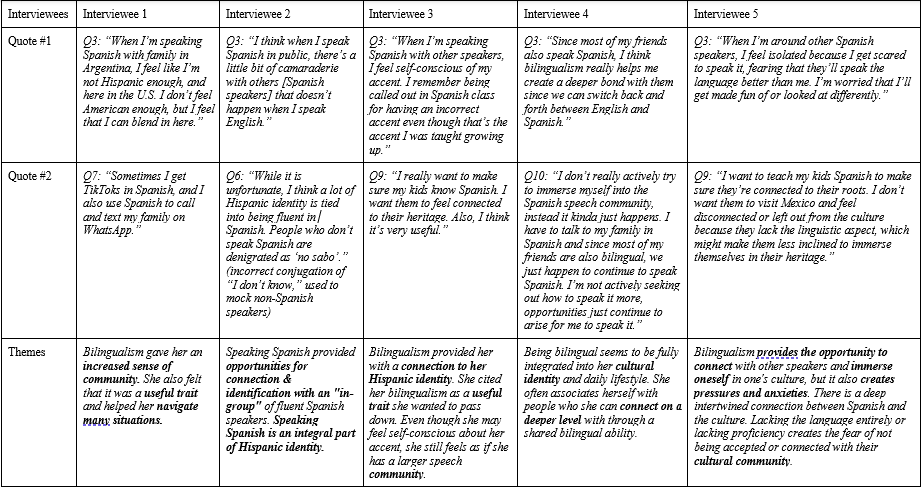
The results of the interviews with bilinguals were quite illustrative in relation to social connections through their first language. Using direct quotes from interviews, many of the answers were quite straightforward:
INTERVIEW 1 – BILINGUAL
I: Did you find it easier to connect and meet people who spoke the same language as you?
J: Yes, most definitely. Uhm, I really liked connecting with people who also spoke Vietnamese because there were a lot of like, you know, Vietnamese language jokes that only Vietnamese people would get.
INTERVIEW 2 – BILINGUAL
I: Have you found it easier to connect with people who speak the same language as you?
S: […] Definitely, yeah. It’s much easier. I mean, it really depends on the person. I wouldn’t say, “Oh, I’m going to go and make friends with whoever speaks Farsi”, because some people, it depends on how approachable they are or if I vibe with them. But in terms of, uh, having one thing to connect. Yes, I would say it’s much easier for me to connect to someone who speaks the same language versus non-Farsi.
INTERVIEW 3 – BILINGUAL
I: Do you find it easier to connect with people who speak the same language(s) as you?
E: Definitely, I feel like it’s easier if I can also speak your language and understand what I’m saying.
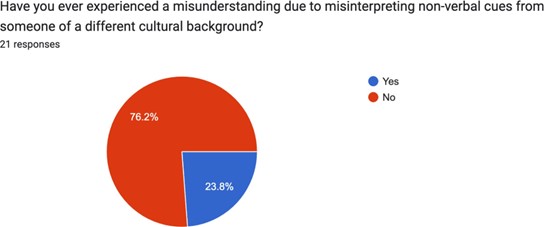
Very consistently across bilingual speakers that we interviewed, sharing a language and culture was essential for forming social ties. They expressed feeling at ease with people who spoke their own language, or how being among a bilingual speaker enhanced their experience more than it would be otherwise.
INTERVIEW 1 – MONOLINGUAL
I: Do you think language or culture has any bearing on who you choose to interact with in your day to day life?
A: Uhm, I definitely would say so… it’s easier for me to talk to or be around someone who has the same language and culture as me.
INTERVIEW 2 – MONOLINGUAL
I: Do you think language or culture has any bearing on who you choose to interact with in your day to day life?
J: […] It kinda sounds like an asshole thing to say– but I think that I’m accepting of a lot of different cultures and stuff– I think there are some subconscious elements, but I wouldn’t know what they were, there are probably some groups I don’t interact with just off of, I don’t know, vibes…
Monolinguals, in their parallel questions to the bilingual speakers, hedged a little when answering but definitely seemed to be likewise confident that they preferred to stay within their own clade of language and culture.
When it came to the respective groups, bilinguals occasionally went out of their way to specifically connect with their own cultures (the interviewee of Interview 1 professed to specifically looking for Southeast Asian clubs on campus in order to connect with others and make friends) but monolinguals had no such compunctions (no one we interviewed was, for instance, attending an “Born American Student” or “Monolingual English” club, nor did such a thing exist). When it came to making friendships, typically they went for shared hobbies unrelated to culture (in one case, gaming clubs).
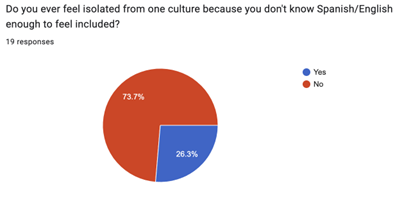
This is not a zero sum game, however– in many cases, bilinguals at UCLA had the added benefit of being able to draw on their extra language in addition to monolingual strategies, meaning their opportunities for friendships were more diverse than the monolingual opportunities. Though the potential for exclusion from these more monolingual-oriented experiences is possible, rejection by monolingual speakers for language or culture was rare, if existent at all.
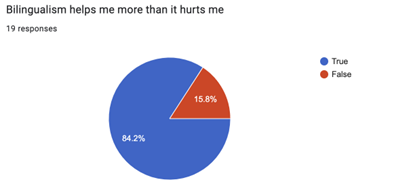
Many of the monolinguals we interviewed wished they had the opportunity to learn other languages and be fluent in them, viewing their English exclusion as a missed opportunity; only one subject of interview wanted to remain a monolingual, though when pressed admitted he would like to learn American Sign Language (and advocated that the rest of the US did, as well) and wasn’t sure if that counted as being multilingual. Broadly speaking in our interviews, bilinguals were happy to provide a social bridge for monolingual to monolingual interactions and delighted to get the chance to share their culture or language with others. No one regretted being bilingual or thought it made their social opportunities at UCLA worse.

Conclusion
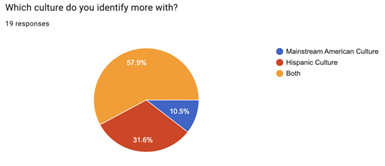
A primary finding that stood out in our research was the absence of in-group/out-group biases within both groups. Instead, we found that linguistic diversity among the population created opportunities for cultural exchange and that in-group preferences did not completely discourage students from reaching out to other cultures. Our results revealed that bilingual students expressed stronger social ties to their cultural communities compared to their monolingual counterparts who conversely expressed a strong desire for second-language acquisition.
These findings led us to conclude that: (1) linguistic diversity can foster a positive school environment by providing opportunities for cultural exchange among different cultures, (2) in-group/out-group biases do not pose negative effects on social relationships among bilingual and monolingual students, (3) bilingualism and second-language acquisition can potentially enhance the social experience of students.
However, these findings are limited by several factors within our study. Firstly, our population of study is representative of a unique environment with a relatively higher proportion of politically liberal, ethnically diverse students than the average American university. Our research is also limited to the study of English-speaking students, restricting our data from being representative of environments with speakers of different dominant languages. Given these limitations, we believe that linguistic diversity thrives most successfully in diverse environments wherein cultural exchange is a social norm and speakers are collectively open-minded to learning
We believe that our findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the importance of second-language acquisition in childhood development to enhance social connections in adulthood and potential positive effects of bilingualism in combating cultural differences in diverse settings. Furthermore, these findings highlight the importance of language knowledge of one’s own culture in strengthening community ties and individual identity. We believe that future research in bilingual and monolingual differences should focus on studying the potential positive effects of second-language acquisition on social skills, educational development, and in overcoming cultural differences.
References
Byers‐Heinlein, K., Behrend, D. A., Said, L. M., Girgis, H., & Poulin‐Dubois, D. (2016). Monolingual and bilingual children’s social preferences for monolingual and bilingual speakers. Developmental Science, 20(4). https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12392
Toppelberg, C. O., & Collins, B. A. (2010). Language, culture, and adaptation in immigrant children. Child and adolescent psychiatric clinics of North America, 19(4), 697–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2010.07.003
Wang, L., Gonzalez, P. D., Lau, P. L., Vaughan, E. L., & Costa, M. F. (2023). “Dando gracias”: Gratitude, social connectedness, and subjective happiness among bilingual Latinx college students. Journal of Latinx Psychology, 11(3), 203-219. https://doi.org/10.1037/lat0000227
Sebanc, A. M., Hernandez, M. D., & Alvarado, M. (2009). Understanding, Connection, and Identification: Friendship Features of Bilingual Spanish-English Speaking Undergraduates. Journal of Adolescent Research, 24(2), 194-217. https://doi.org/10.1177/0743558408329953
Xu, C. L. (2022). Portraying the ‘Chinese international students’: a review of English-language and Chinese-language literature on Chinese international students (2015–2020). Asia Pacific Education Review, 23(1), 151–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12564-021-09731-8