All Jokes Aside – Indexing Gender and Race in Stand-Up Comedy
Ammi Lane-Volz, Cate Dark, Ava Kaiser, Grace Shoemaker, Alex Farfan
As playful and harmless as something titled “comedy” can seem, the political and cultural implications of what is deemed funny are not insignificant. From stand-up performance to jokes around the water cooler, comedy is used as a tool to socially bond, establish hierarchy, critique global affairs, and index identity. Our project set out to explore how stand-up comedians index their identities through mimicry, contrast, and slurs, specifically focusing on how they index themselves as part of versus separate from gendered and racial groups. We studied the specials of ten stand-up comedians from the Netflix series The Standups to see if they more often tended to align their identities through references to their own demographics (in-group indexing) or through references to outside groups (out-group indexing). We found several patterns that emerged, including higher instances of non-white comedians mentioning their race (three times more often), 60% of which consisted of in-group indexing. We also found the opposite to be true for gender, with men referencing gender almost twice as often as the female comedians, 55% of which consisted of out-group indexing. These patterns invite several follow-up questions on the different tactics comedians use when writing their sets and how their choices might be influenced by their place in society and membership of different social majority or minority groups.
Introduction and Background
Comedy holds significant cultural influence, serving both as a mirror reflecting societal norms and as a tool for challenging them. We identified a notable gap in research relating to how stand-up comedians utilize their demographic backgrounds. A study done on representations of race and gender within Comedy Central programming found that although the channel has made an effort to expand its brand by employing more female and racially diverse comedians, the type of jokes found within these skits reinforce power dynamics and white heteronormative masculinity (Marx 2016). Another study on stand-up comedy and cultural spread argued that stand-up comedians are able to reinforce and/or challenge existing cultural stereotypes through their sets, both within the comedic monologues themselves and in the audience’s minds (Yus 2002). Based on this research, it is evident that a comedian’s own demographic information, specifically gender and race, can play a role in the creation or reinforcement of stereotypes in comedy. Yet none of these studies discuss the ways in which comedians index their own demographics. To fill this gap, we wanted to answer the question of how comedians navigate indexing their identities by looking at the frequency of in-group versus out-group demographic references and how these references connect to broader social contexts.
Methods
For our analysis, we chose to look at ten thirty-minute stand-up specials from seasons two and three of the Netflix series The Standups. Each episode of this show focuses on a different stand-up comedian. Comedians from this show are of moderate acclaim, meaning their sets are polished (i.e. representative of a “standard” professional stand-up comedian) but the researchers and the general public may not know the comedians by name. Choosing specials from this show allowed for some standardization of the audience and venue, and provided us with a broader view of multiple professional stand-up comedians than just analyzing one or two longer specials.
Each researcher looked at two randomly chosen specials and noted each time that a comedian mentioned their own identity demographic (race, gender, sexuality, political affiliation, class, and age) and each time they made a comparison to another demographic. These comparisons included strategies like direct comparison or mimicry of another demographic’s accent or physical mannerisms. We also noted each time a comedian said a slur related to their own identity demographic and each time they said a slur related to a different demographic. Based on our preliminary data, we decided to whittle down our focus from the six demographic categories mentioned above to just race and gender. Within these categories, we split them into white vs. marginalized racial identity and men vs. women, respectively. It is also important to note that our sample was evenly split in terms of gender (five men, five women) and race (five white comedians, five comedians of color).
Data and Analysis
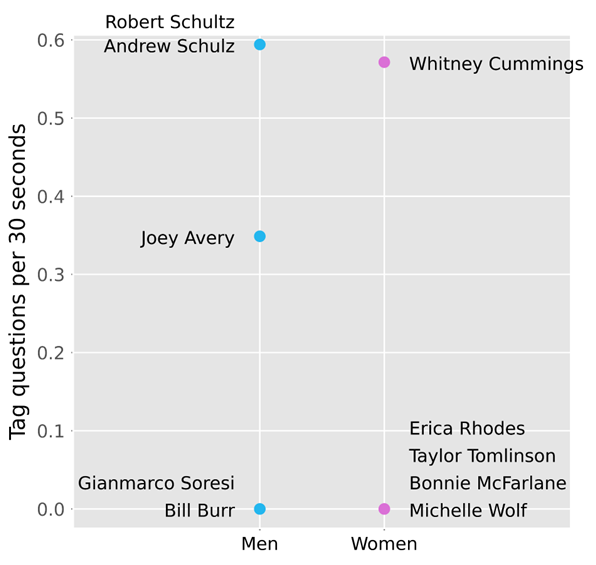
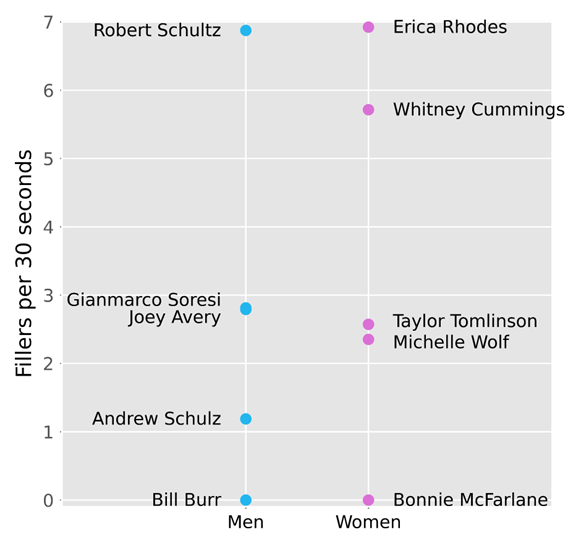
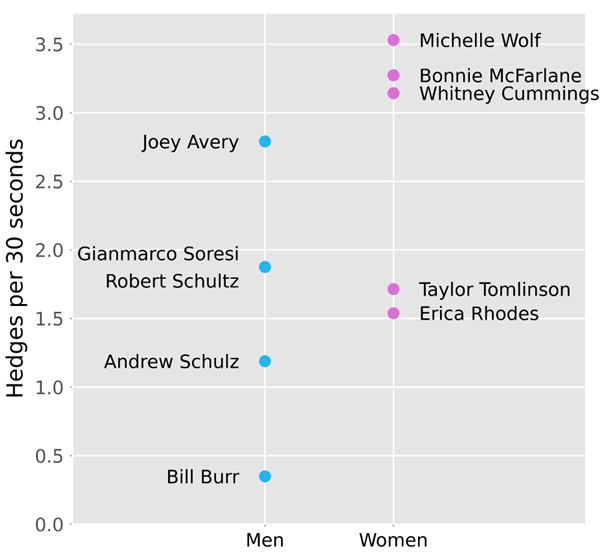
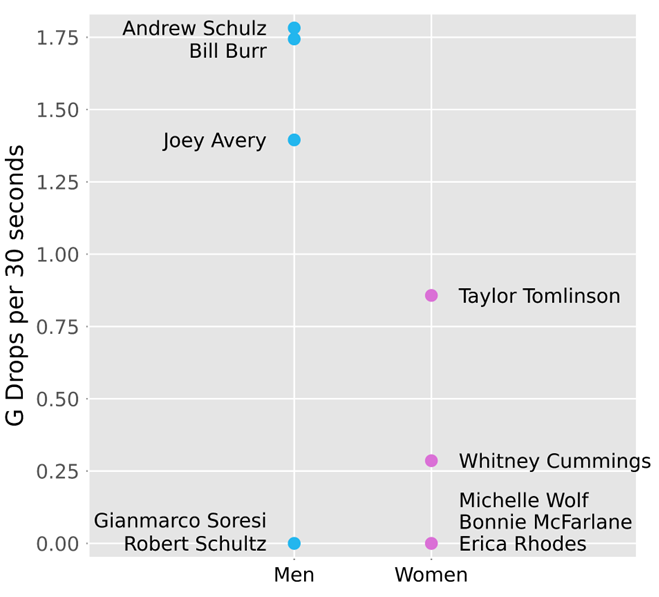
Using the data we collected for each comedian, we generated the following figures that summarize our findings:
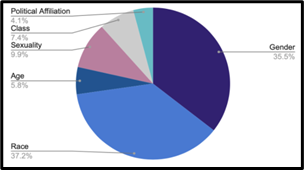
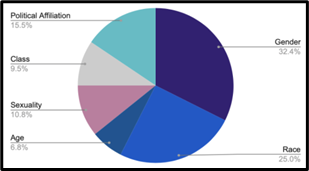
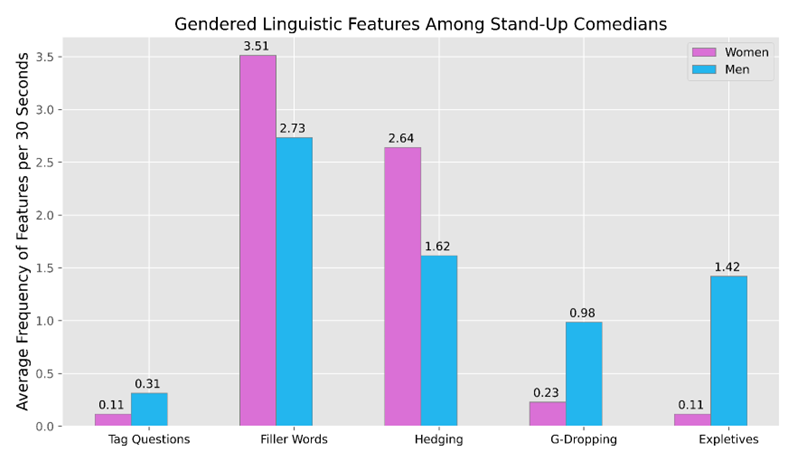
As seen in Figure 1 and Figure 2, comedians tend to reference and compare their gender and race significantly more than age, class, sexuality, or political affiliation. Using this information, we were able to narrow our analysis to focus on this key demographic data.
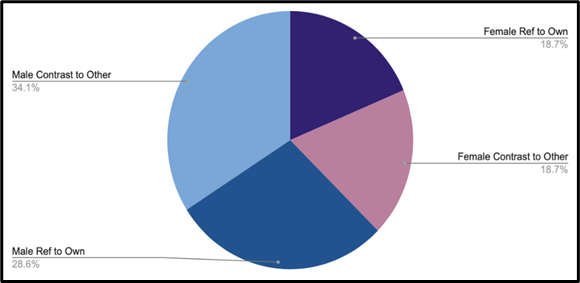
Figure 3 demonstrates that male comedians were much more likely to reference gender to index their identities, with comparison to another gender being the most common reference type.
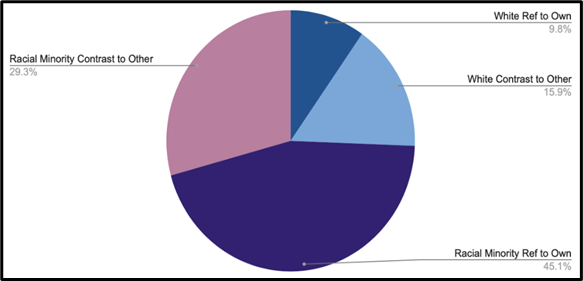
Figure 4 indicates that racial minority comedians referenced race about three times more than white comedians, with references to their own race being the most common reference type.
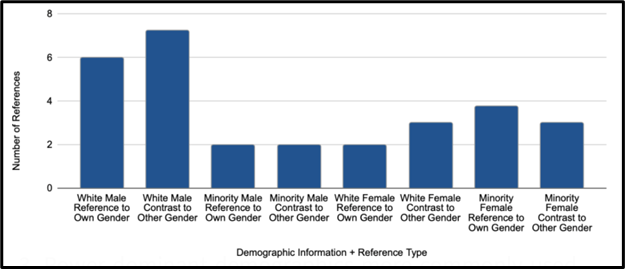
Figure 5 indicates that white men were about two times more likely to reference gender than any other demographic combination.
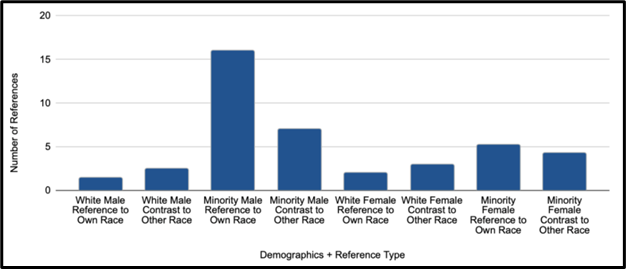
Figure 6 shows that minority men were three times more likely to reference their own race than any other combination of race and gender.
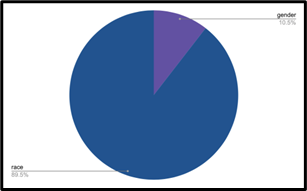
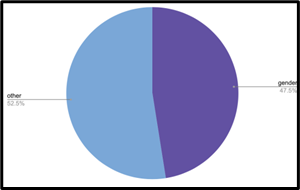
Figure 7 shows the large majority of self-referential demographic slurs were race-related, as Black comedians tended to use the n-word multiple times in their sets. Figure 8 shows that out-group related demographic slurs were slurs related to gender and other demographics; none were race-related.
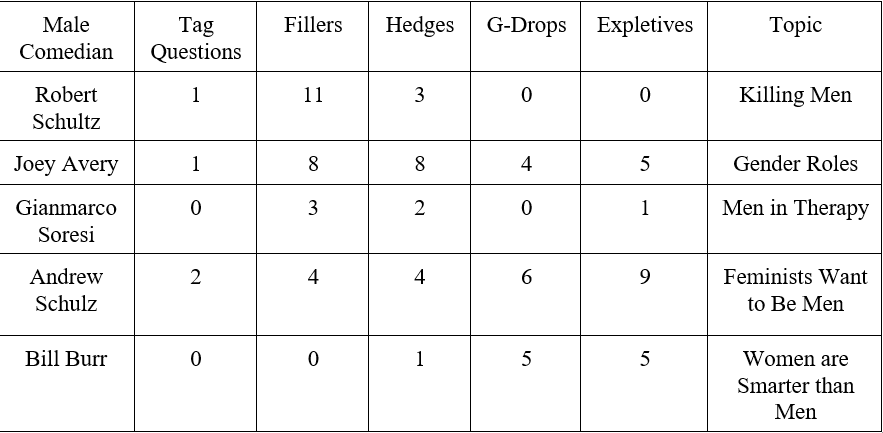
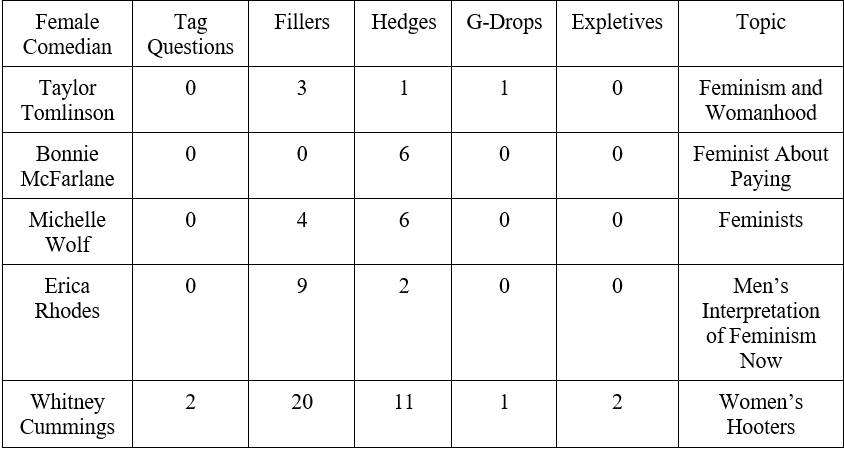
Raw Data
Discussion
Based on our data and outside research, the frequency with which comedians index their race and gender within their sets may be linked to a few different social phenomena.
The finding that white men are more likely to index their gender identity in their comedic routines may suggest that male comedians feel compelled to incorporate their gender identity into their comedy routines, or that they find this to be more socially acceptable than women. This could reflect broader gender expectations where men are often encouraged to assert their masculinity or draw attention to their gender in public spaces (McVittie et al., 2017). Racial minority comedians’ tendency to reference their minority status could indicate a desire to confront stereotypes, draw attention to racial issues, or establish a unique comedic identity. This could stem from personal experiences of marginalization or a sense of responsibility to address racial dynamics in their performances (Sullivan et al., 2021). Additionally, the observation that power dominant demographics (white, men) more commonly used comparison than their marginalized counterparts could imply that those in positions of power feel more comfortable using comparison as a comedic tool. This could be because they have greater societal latitude to freely express themselves without fear of repercussions (Tobore, 2023). By using comparison, minority comedians risk reinforcing existing power dynamics and societal hierarchies where masculinity and whiteness are considered the norm. For a minority comedian, refraining from such comparisons can be a way to affirm their own racial or cultural identity without centering whiteness as a point of reference. Finally, the fact that gendered slurs were employed by out-group comedians, while race based slurs were only used by in-group racial minority comedians suggests a greater societal awareness or sensitivity towards racial issues than gender issues. This may stem from a recognition of the historical and ongoing harm caused by racial slurs (Wilson, 2020). Overall, our findings underscore how the comedy stage becomes a microcosm for broader societal interactions and power relations. The act of indexing one’s identity in comedy can serve as a means of negotiating power, identity, and belonging within a societal context that is stratified along lines of race, gender, and sexuality.
In general, comedy does not merely reflect the social order but actively participates in its construction and perpetuation. The comedian’s role in creating a “social contract” with the audience, wherein their narratives and identities are validated, highlights the performative aspect of social identity and the power of narrative in shaping reality. The audience is also not merely a passive receiver of comedy; they have agency in choosing where to laugh and where not to laugh. They are then an active participant in the co-creation of the comedic experience and, by extension, the social norms and power dynamics it reinforces or challenges.
Conclusion
This research underscores the potential of comedy as a site of social commentary and critique. While comedy can perpetuate stereotypes and power imbalances, it also holds the potential for subversion. Comedians who are aware of the power dynamics at play in their performances can use humor to challenge societal norms, question stereotypes, and imagine new ways of being.
In framing our findings within the broader context of power relations, language, and agency, we contribute to a deeper understanding of the role of comedy in society. This opens up important discussions about the responsibilities of comedians and audiences alike in shaping the social discourse through humor. It also suggests avenues for further research into how comedy can be used as a tool for social change, by both reinforcing and challenging the status quo.
References
Marx, N. (2016). Expanding the brand: Race, gender, and the post-politics of representation on Comedy Central. Television & New Media, 17(3), 272–287. https://doi.org/10.1177/1527476415577212
Miller, T. (Producer). (2017-2021). The Standups [TV Series]. Netflix. https://www.netflix.com/browse?jbv=80175685
McVittie, C., Hepworth, J., & Goodall, K. (2017). Masculinities and health. The Psychology of Gender and Health, 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-803864-2.00004-3
Sullivan, J. N., Eberhardt, J. L., & Roberts, S. O. (2021). Conversations about race in black and white US families: Before and after George Floyd’s death. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(38). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106366118
Tobore, T. O. (2023). On power and its corrupting effects: The effects of power on human behavior and the limits of Accountability Systems. Communicative & Integrative Biology, 16(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/19420889.2023.2246793
Wilson, C. (2020, October 4). N-word: The troubled history of the racial slur. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/stories-53749800
Yus, Francisco. (2002). Stand-up comedy and cultural spread: The case of sex roles. Babel A.F.I.A.L.. special issue on humour studies. 245-294. https://personal.ua.es/francisco.yus/site/Afial.pdf